If the atomic number of an element is 6 and its mass number is 14, how many neutrons are contained in the nucleus? Answers (2) Xander Wolf 21 March, 19:01. This is a list of the 118 chemical elements which have been identified as of 2021. A chemical element, often simply called an element, is a species of atoms which all have the same number of protons in their atomic nuclei (i.e., the same atomic number, or Z). As we know Mass number means sum of total numbers of protons and nutrons present in nucleus of an atom. As we know atomic number means number of protons present in nucleus of an atom.
The elements of the periodic table sorted by atomic number

click on any elements name for further chemical properties, environmental data or health effects.
This list contains the 118 elements of chemistry.

| The chemical elements of the periodic chart sorted by: | Atomic number | Name chemical element | Symbol |
| - Name alphabetically | 1 | Hydrogen | H |
| - Atomic number | 2 | Helium | He |
| - Symbol | 3 | Lithium | Li |
| - Atomic Mass | 4 | Beryllium | Be |
| - Electronegativity | 5 | Boron | B |
| - Density | 6 | Carbon | C |
| - Melting point | 7 | Nitrogen | N |
| - Boiling point | 8 | Oxygen | O |
| - Vanderwaals radius | 9 | Fluorine | F |
| - Year of discovery | 10 | Neon | Ne |
| - Inventor surname | 11 | Sodium | Na |
| - Elements in earthcrust | 12 | Magnesium | Mg |
| - Elements in human body | 13 | Aluminum | Al |
| - Covalenz radius | 14 | Silicon | Si |
| - Ionization energy | 15 | Phosphorus | P |
For chemistry students and teachers: The tabular chart on the right is arranged by Atomic number. The first chemical element is Hydrogen and the last is Ununoctium. Please note that the elements do not show their natural relation towards each other as in the Periodic system. There you can find the metals, semi-conductor(s), non-metal(s), inert noble gas(ses), Halogens, Lanthanoides, Actinoids (rare earth elements) and transition metals. | 16 | Sulfur | S |
| 17 | Chlorine | Cl | |
| 18 | Argon | Ar | |
| 19 | Potassium | K | |
| 20 | Calcium | Ca | |
| 21 | Scandium | Sc | |
| 22 | Titanium | Ti | |
| 23 | Vanadium | V | |
| 24 | Chromium | Cr | |
| 25 | Manganese | Mn | |
| 26 | Iron | Fe | |
| 27 | Cobalt | Co | |
| 28 | Nickel | Ni | |
| 29 | Copper | Cu | |
| 30 | Zinc | Zn | |
| 31 | Gallium | Ga | |
| 32 | Germanium | Ge | |
| 33 | Arsenic | As | |
| 34 | Selenium | Se | |
| 35 | Bromine | Br | |
| 36 | Krypton | Kr | |
| 37 | Rubidium | Rb | |
| 38 | Strontium | Sr | |
| 39 | Yttrium | Y | |
| 40 | Zirconium | Zr | |
| 41 | Niobium | Nb | |
| 42 | Molybdenum | Mo | |
| 43 | Technetium | Tc | |
| 44 | Ruthenium | Ru | |
| 45 | Rhodium | Rh | |
| 46 | Palladium | Pd | |
| 47 | Silver | Ag | |
| 48 | Cadmium | Cd | |
| 49 | Indium | In | |
| 50 | Tin | Sn | |
| 51 | Antimony | Sb | |
| 52 | Tellurium | Te | |
| 53 | Iodine | I | |
| 54 | Xenon | Xe | |
| 55 | Cesium | Cs | |
| 56 | Barium | Ba | |
| 57 | Lanthanum | La | |
| 58 | Cerium | Ce | |
| 59 | Praseodymium | Pr | |
| 60 | Neodymium | Nd | |
| 61 | Promethium | Pm | |
| 62 | Samarium | Sm | |
| 63 | Europium | Eu | |
| 64 | Gadolinium | Gd | |
| 65 | Terbium | Tb | |
| 66 | Dysprosium | Dy | |
| 67 | Holmium | Ho | |
| 68 | Erbium | Er | |
| 69 | Thulium | Tm | |
| 70 | Ytterbium | Yb | |
| 71 | Lutetium | Lu | |
| 72 | Hafnium | Hf | |
| 73 | Tantalum | Ta | |
| 74 | Tungsten | W | |
| 75 | Rhenium | Re | |
| 76 | Osmium | Os | |
| 77 | Iridium | Ir | |
| 78 | Platinum | Pt | |
| 79 | Gold | Au | |
| 80 | Mercury | Hg | |
| 81 | Thallium | Tl | |
| 82 | Lead | Pb | |
| 83 | Bismuth | Bi | |
| 84 | Polonium | Po | |
| 85 | Astatine | At | |
| 86 | Radon | Rn | |
| 87 | Francium | Fr | |
| 88 | Radium | Ra | |
| 89 | Actinium | Ac | |
| 90 | Thorium | Th | |
| 91 | Protactinium | Pa | |
| 92 | Uranium | U | |
| 93 | Neptunium | Np | |
| 94 | Plutonium | Pu | |
| 95 | Americium | Am | |
| 96 | Curium | Cm | |
| 97 | Berkelium | Bk | |
| 98 | Californium | Cf | |
| 99 | Einsteinium | Es | |
| 100 | Fermium | Fm | |
| 101 | Mendelevium | Md | |
| 102 | Nobelium | No | |
| 103 | Lawrencium | Lr | |
| 104 | Rutherfordium | Rf | |
| 105 | Dubnium | Db | |
| 106 | Seaborgium | Sg | |
| 107 | Bohrium | Bh | |
| 108 | Hassium | Hs | |
| 109 | Meitnerium | Mt | |
| 110 | Darmstadtium | Ds | |
| 111 | Roentgenium | Rg | |
| 112 | Copernicium | Cn | |
| 113 | Nihonium | Nh | |
| 114 | Flerovium | Fl | |
| 115 | Moscovium | Mc | |
| 116 | Livermorium | Lv | |
| 117 | Tennessine | Ts | |
| 118 | Oganesson | Og |
Click here: for a schematic overview of the periodic table of elements in chart form
Do you need to know the weight of some molecules? Try our Molecular Weight Calculator!
Please report any accidental mistake in the above statistics on chemical elements
Lenntech (European Head Office)
Distributieweg 3
2645 EG Delfgauw
The Netherlands
Phone: +31 152 610 900
fax: +31 152 616 289
e-mail: info@lenntech.com
Lenntech USA LLC (Americas)
5975 Sunset Drive
South Miami, FL 33143
USA
Phone: +1 877 453 8095
e-mail: info@lenntech.com
Atomic Number 65
Lenntech DMCC (Middle East)
Level 5 - OFFICE #8-One JLT Tower
Jumeirah Lake Towers
Dubai - U.A.E.
Phone: +971 4 429 5853
e-mail: info@lenntech.com
Element With Atomic Number 17
Copyright © 1998-2021 Lenntech B.V. All rights reserved
Learning Outcomes
- Define atomic and mass numbers.
- Determine the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in an atom.
- Identify the charge and relative mass of subatomic particles.
- Label the location of subatomic particles in the atom.
- Determine the mass of an atom based on its subatomic particles.
- Write A/Z and symbol-mass format for an atom.
Atoms are the fundamental building blocks of all matter and are composed of protons, neutrons, and electrons. Because atoms are electrically neutral, the number of positively charged protons must be equal to the number of negatively charged electrons. Since neutrons do not affect the charge, the number of neutrons is not dependent on the number of protons and will vary even among atoms of the same element.
Atomic Number
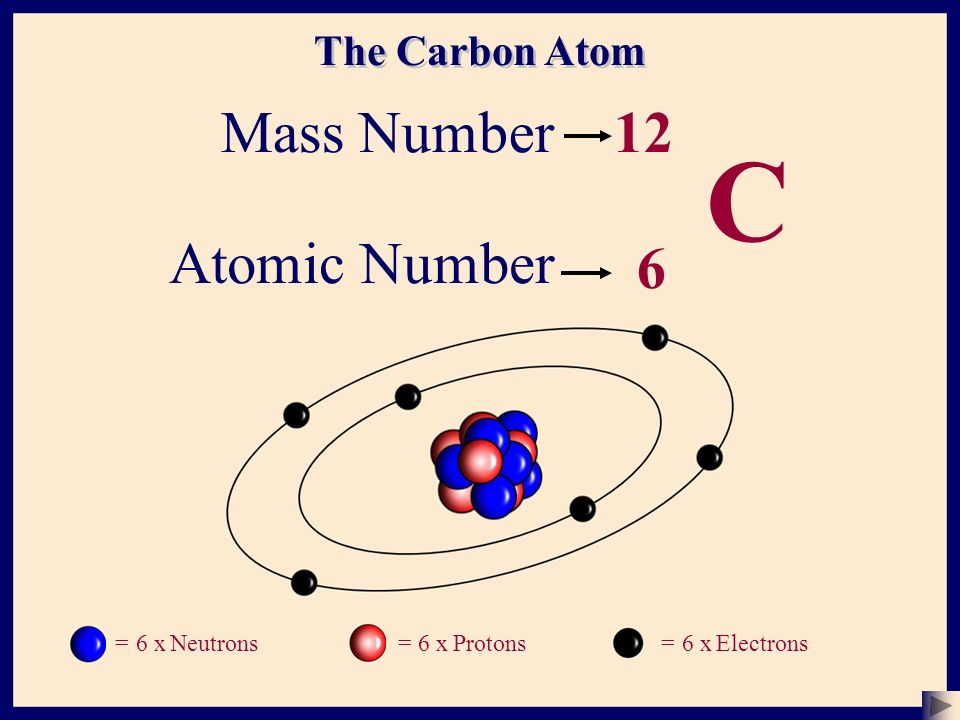
The atomic number (represented by the letter Z)of an element is the number of protons in the nucleus of each atom of that element. An atom can be classified as a particular element based solely on its atomic number. For example, any atom with an atomic number of 8 (its nucleus contains 8 protons) is an oxygen atom, and any atom with a different number of protons would be a different element. The periodic table (see figure below) displays all of the known elements and is arranged in order of increasing atomic number. In this table, an element's atomic number is indicated above the elemental symbol. Hydrogen, at the upper left of the table, has an atomic number of 1. Every hydrogen atom has one proton in its nucleus. Next on the table is helium, whose atoms have two protons in the nucleus. Lithium atoms have three protons, beryllium atoms have four, and so on.
Since atoms are neutral, the number of electrons in an atom is equal to the number of protons. Hydrogen atoms all have one electron occupying the space outside of the nucleus. Helium, with two protons, will have two electrons. In the chemical classroom, the proton count will always be equivalent to an atom's atomic number. This value will not change unless the nucleus decays or is bombarded (nuclear physics).
Mass Number
Experimental data showed that the vast majority of the mass of an atom is concentrated in its nucleus, which is composed of protons and neutrons. The mass number (represented by the letter A)is defined as the total number of protons and neutrons in an atom. Consider the table below, which shows data from the first six elements of the periodic table.
| Name | Symbol | Atomic Number (Z) | Protons | Neutrons | Electrons | Mass Number (A) (rounded to two decimals) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| hydrogen | (ce{H}) | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1.01 |
| helium | (ce{He}) | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 4.00 |
| lithium | (ce{Li}) | 3 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 6.94 |
| beryllium | (ce{Be}) | 4 | 4 | 5 | 4 | 9.01 |
| boron | (ce{B}) | 5 | 5 | 6 | 5 | 10.18 |
| carbon | (ce{C}) | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 12.01 |
Consider the element helium. Its atomic number is 2, so it has two protons in its nucleus. Its nucleus also contains two neutrons. Since (2 + 2 = 4), we know that the mass number of the helium atom is 4. Finally, the helium atom also contains two electrons, since the number of electrons must equal the number of protons. This example may lead you to believe that atoms have the same number of protons and neutrons, but a further examination of the table above will show that this is not the case. Lithium, for example, has three protons and four neutrons, giving it a mass number of 7.
Knowing the mass number and the atomic number of an atom allows you to determine the number of neutrons present in that atom by subtraction.
[text{Number of neutrons} = text{ rounded mass number} - text{atomic number}]
Atoms of the element chromium (left( ce{Cr} right)) have an atomic number of 24 and a mass number of 52. How many neutrons are in the nucleus of a chromium atom? To determine this, you would subtract as shown:
[52 - 24 = 28 : text{neutrons in a chromium atom}]
The composition of any atom can be illustrated with a shorthand notation called A/Z format. Both the atomic number and mass are written to the left of the chemical symbol. The 'A' value is written as a superscript while the 'Z' value is written as a subscript. For an example of this notation, look to the chromium atom shown below:
[ce{^{52}_{24}Cr}]
Another way to refer to a specific atom is to write the mass number of the atom after the name, separated by a hyphen. Symbol-mass format for the above atom would be written as Cr-52. In this notation, the atomic number is not included. You will need to refer to a periodic table for proton values.

Example (PageIndex{1})
Calculate each of the three subatomic particles and give specific group or period names for each atom.
- mercury
- platinum
- bromine
Solutions
- Hg (transition metal)- has 80 electrons, 80 protons, and 121 neutrons
- Pt (transition metal)- has 78 electrons, 78 protons, and 117 neutrons
- Br (halogen)- has 35 electrons, 35 protons, and 45 neutrons
Example (PageIndex{2})
Atomic Number Chart
Write both A/Z and symbol-mass formats for the atoms in Example (PageIndex{1}).
Solutions
- (ce{^{201}_{80}Hg}) and Hg-201
- (ce{^{195}_{78}Pt}) and Pt-195
- (ce{^{80}_{35}Br}) and Br-80
Example (PageIndex{3})
Identify the elements based on the statements below.
- Which element has 25 protons?
- Which element has 0 neutrons?
- Which element has 83 electrons?
Solutions
a. manganese
b. hydrogen
c. bismuth
Atomic Number 6 Element
Need More Practice?
Atomic Number 63
- Turn to section 3.E of this OER and answer questions #1-#2, #4, and #8.
Atomic Number 67
Contributors and Attributions
Atomic Number 6
CK-12 Foundation by Sharon Bewick, Richard Parsons, Therese Forsythe, Shonna Robinson, and Jean Dupon.
Allison Soult, Ph.D. (Department of Chemistry, University of Kentucky)
